When it comes to photo editing, one of the most effective and versatile tools at your disposal is Gaussian Blur. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced photographer, Gaussian Blur can be used to enhance your images with elegance and precision. In this article, we’ll dive into how to use Gaussian Blur to transform your photos, creating smooth, soft-focus effects that add a sense of subtle beauty to your images.
1. What is Gaussian Blur?
Before we dive into how to use Gaussian Blur, it’s essential to understand what it is and why it’s such a popular tool in photography and image editing. Gaussian Blur is a technique used to blur the image, creating a smooth, soft transition between colors and edges. The effect is named after the Gaussian function, a mathematical formula that generates the blur effect by averaging pixel values within a specified radius.
This type of blur is particularly useful because it maintains a natural, organic feel, unlike other blur methods that can create harsh transitions. The result is a soft, aesthetically pleasing image, often used to reduce distractions in the background or to emphasize the subject in focus.
2. Why Use Gaussian Blur?
There are several reasons why Gaussian Blur is such a valuable tool in photo editing. Here are a few key reasons:
Softens Harsh Edges: Gaussian Blur can soften sharp or hard edges in an image, giving it a more polished, professional look.
Focus Attention: It’s frequently used to blur backgrounds, drawing more attention to the subject of the image without distractions.
Creates a Dreamy, Artistic Effect: The blur can give your image a whimsical, dreamlike quality, often used in portrait photography or fine art photography.
Noise Reduction: It’s also effective in reducing graininess or visual noise in images, especially in low-light conditions.
3. How to Apply Gaussian Blur in Different Software
While the specific steps for applying Gaussian Blur will vary slightly depending on the software you’re using, the general concept remains the same. Here’s a breakdown of how to apply Gaussian Blur in some of the most popular image editing tools.
Using Gaussian Blur in Adobe Photoshop:
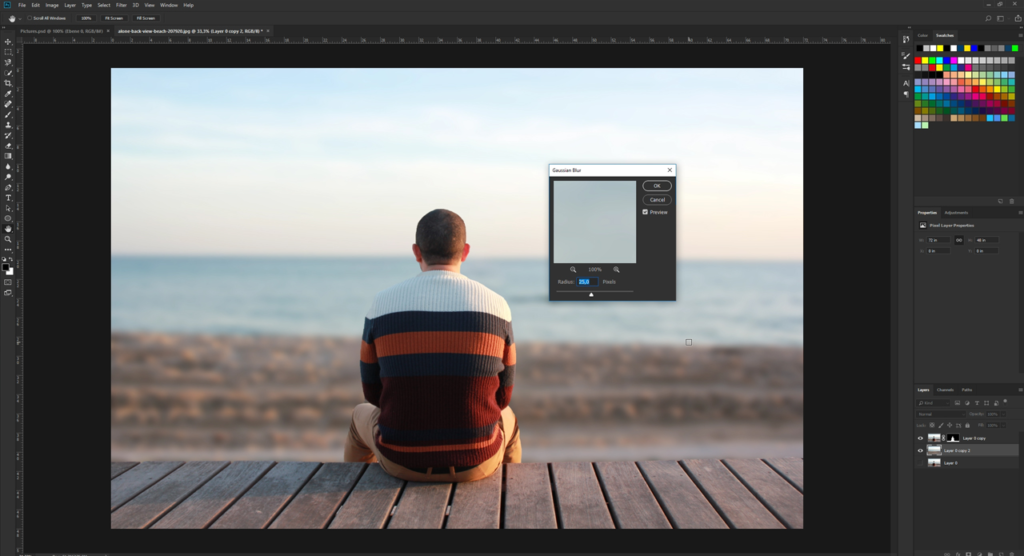
Open your image in Photoshop and duplicate the layer (Ctrl + J) to keep the original safe.
Select the duplicated layer.
Go to the Filter menu, choose Blur, and then select Gaussian Blur from the dropdown.
A dialog box will appear. Adjust the Radius slider to control the intensity of the blur. The higher the radius, the more blurred the image becomes.
Click OK to apply the effect.
Using Gaussian Blur in Lightroom:
While Lightroom doesn’t have a dedicated Gaussian Blur filter, you can still achieve a similar effect by using the Radial Filter tool to blur specific areas of the image. Adjusting the sharpness and clarity sliders also helps you achieve a soft focus effect.
Using Gaussian Blur in GIMP (Free Software):
Open your image in GIMP.
Select the layer or area you wish to blur.
Go to the Filters menu, choose Blur, and then Gaussian Blur.
Adjust the Horizontal and Vertical blur radii, and click OK.
Using Gaussian Blur in Affinity Photo:
Open your image in Affinity Photo.
Select the area you want to blur or the entire image.
Go to the Filters menu, select Blur, and then Gaussian Blur.
Adjust the Radius to fine-tune the blur amount, and click Apply.
4. Tips for Using Gaussian Blur for Elegant Enhancements
To make sure you’re using Gaussian Blur to its full potential, here are a few tips to apply it elegantly without overdoing it:
Use it subtly: The key to elegance with Gaussian Blur is subtlety. Avoid over-blurring your image. Instead, apply a slight blur to backgrounds or outer edges while keeping the main subject crisp and sharp.
Layering Effects: Sometimes, you may want to blur a portion of the image while keeping the rest of the image sharp. In this case, use a mask to apply the blur to specific areas of the photo. This gives you more control over the final effect.
Avoid the entire image: Applying Gaussian Blur to the entire image might result in a flat, unappealing photo. Instead, focus on certain parts of the image like the background, edges, or areas with excessive noise.
Focus on the background: One of the most popular uses of Gaussian Blur is to blur backgrounds, creating a bokeh effect. This makes your subject stand out and appear more focused, enhancing the overall composition.
Layer your blur effect: If you need more control, consider duplicating your layer and applying a stronger blur to one layer while keeping the other layer sharp. This can help you create a more refined, polished effect.
5. Common Mistakes to Avoid
While Gaussian Blur is a great tool, it’s important to avoid some common mistakes when using it:
Excessive Blurring: It’s tempting to apply a strong blur to hide imperfections, but too much blur can make your image look unnatural. Always err on the side of caution and test different blur levels.
Overuse in Portraits: While a light blur in portraiture can add a dreamy effect, too much blur can make faces and other details appear washed out or fuzzy. Keep key facial features sharp.
Not Using Layers: Applying Gaussian Blur directly to your image without using layers or masks can make it difficult to make adjustments later. Always use a separate layer or duplicate your image for flexibility.
6. Use Cases for Gaussian Blur

Here are some scenarios where Gaussian Blur can be a game-changer for your images:
Portrait Photography: Use Gaussian Blur to soften the background and bring more focus to the subject’s face.
Landscape Photography: Apply subtle Gaussian Blur to distant elements in your landscape shots to create a sense of depth.
Product Photography: Gaussian Blur can help isolate your product from the background, giving it more prominence.
Graphic Design: Whether for logos, banners, or social media images, Gaussian Blur can add a professional touch to your designs, especially when used with layered text and graphics.
(FAQs) About Using Gaussian Blur
1. What is the best radius for applying Gaussian Blur?
The best radius depends on the size of your image and the effect you’re aiming for. A radius of 2-5 pixels is ideal for subtle blurring, while a higher radius (10-20 pixels) will create a more pronounced blur effect. Always preview the effect before finalizing it.
2. Can I undo Gaussian Blur if I overdo it?
Yes! If you’re using non-destructive editing techniques (such as layers or smart objects), you can easily adjust or remove the Gaussian Blur effect. In Photoshop, for example, you can use the History Panel to go back to an earlier version of the image.
3. How does Gaussian Blur compare to other types of blur?
Unlike motion blur or lens blur, which simulate specific types of focus or movement, Gaussian Blur is more neutral and creates a smooth, uniform blur. It’s often preferred for its natural, subtle look.
4. Can Gaussian Blur reduce noise in an image?
Yes, Gaussian Blur can help reduce noise or grain in an image by smoothing out pixel variations. However, be cautious with the intensity, as too much blur can cause a loss of important details.
5. Can I use Gaussian Blur for creative effects?
Absolutely! Gaussian Blur can be used creatively in various ways, such as creating a soft-focus effect for portraits, isolating a subject from the background, or even applying it to shapes and text in graphic design to add an ethereal look.
Read Next: How to Look Great on Video: Outfit Suggestions for Your Company Shoot
For More More Visit: Pulses Magazines





























































